Human Behavior Recognition
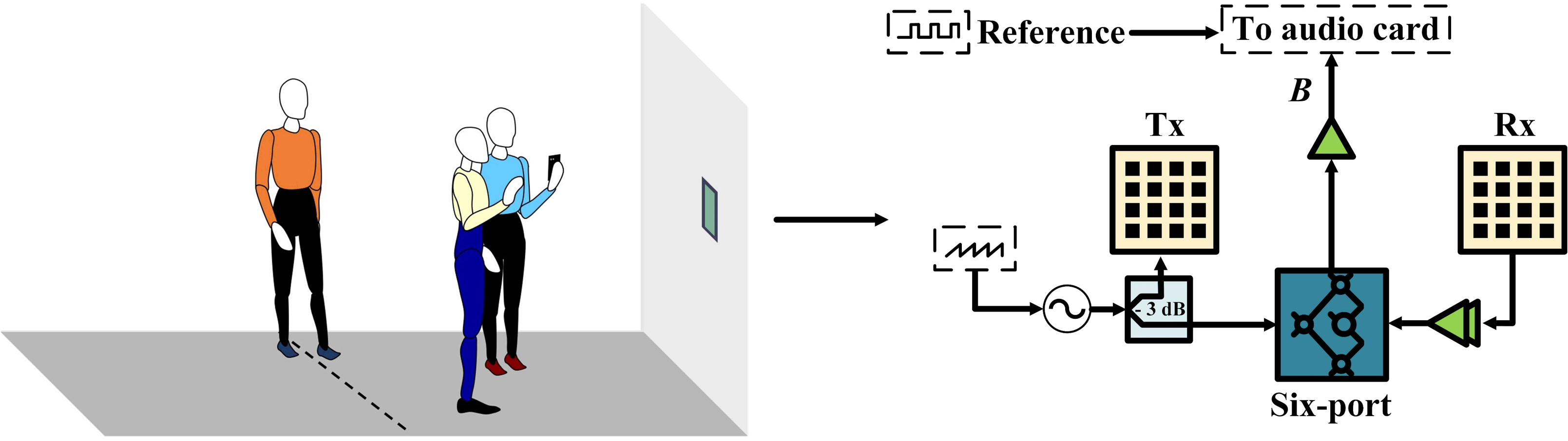 Medical studies suggest that physical activity lowers the risks of serious health problems, such as heart disease, depression, and dementia. Hand gestures are probably the most intuitive way to communicate in a nonverbally manner. They can be used to remotely control electronic devices such as cell phones, smart watches, TVs, and personal computers. Towards this end, I have studied the use of frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) radars for physical activity recognition and hand gesture identification in multi-person scenarios. To date, most of similar applications only consider scenarios with one human being in the scene. The proposed approaches benefitted from the range discrimination capability of FMCW radars and spectral power to differentiate the exercises and the hand gestures of interest from other interferences.
Medical studies suggest that physical activity lowers the risks of serious health problems, such as heart disease, depression, and dementia. Hand gestures are probably the most intuitive way to communicate in a nonverbally manner. They can be used to remotely control electronic devices such as cell phones, smart watches, TVs, and personal computers. Towards this end, I have studied the use of frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) radars for physical activity recognition and hand gesture identification in multi-person scenarios. To date, most of similar applications only consider scenarios with one human being in the scene. The proposed approaches benefitted from the range discrimination capability of FMCW radars and spectral power to differentiate the exercises and the hand gestures of interest from other interferences.
Oportunistic RF Sensing
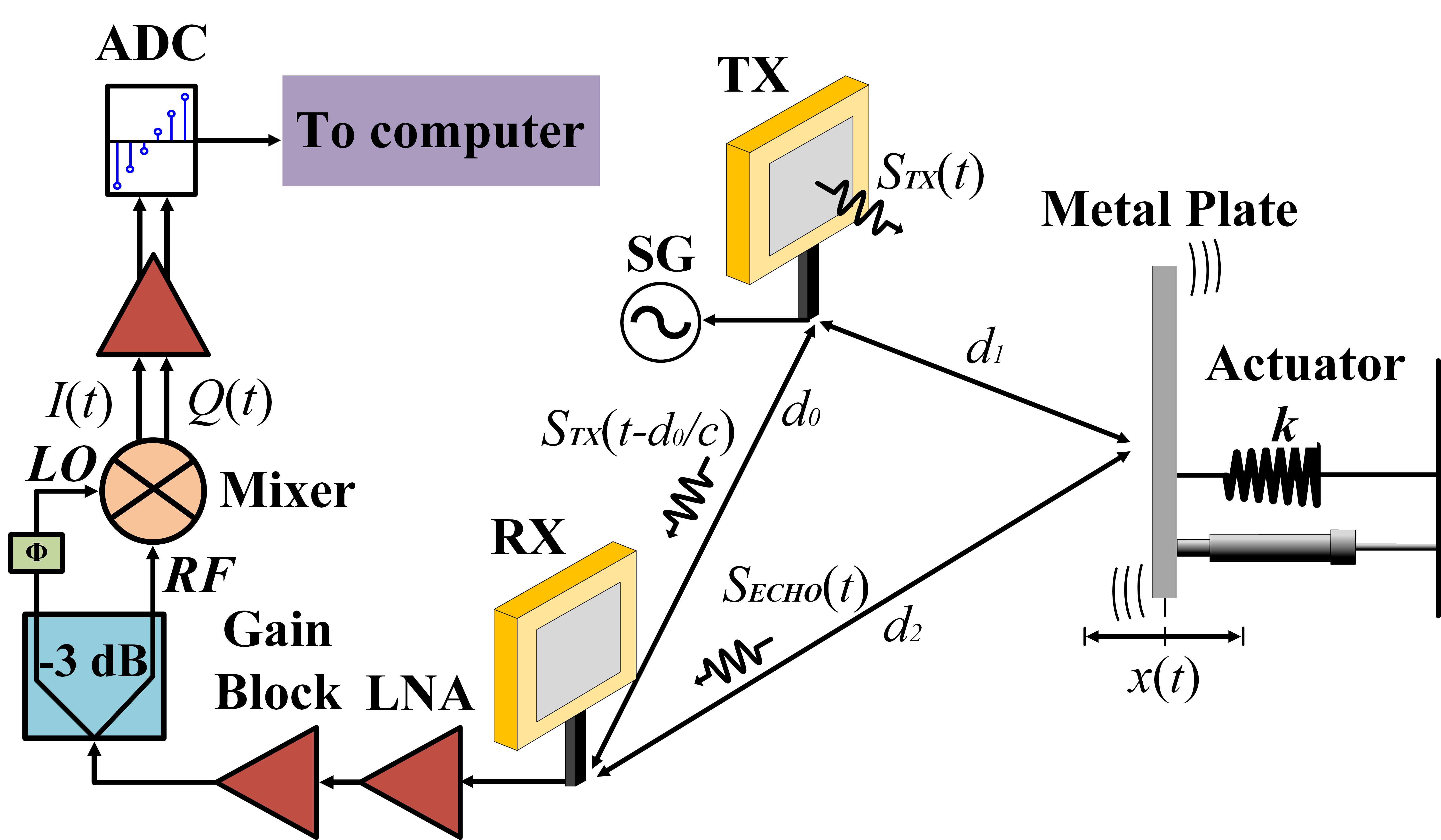 The use of opportunistic RF sensors has a long history in military applications, airspace surveillance, and air traffic management. Passive or opportunistic microwave sensing devices detect and track targets by simultaneously analyzing the direct-path signals emitted from RF sources and the signals scattered from targets of interest. Because of the popularization of indoor communication networks, it is advantageous to design sensing systems that leverage ubiquitous signals transmitted by third-party transmitters. Furthermore, passive sensing technologies are a great alternative to avoid interference among different transceivers and to contribute to efficient spectrum usage. In contrast to most of the current results on indoor passive sensing that rely on existing hardware architectures exclusively designed for wireless communication purposes, I proposed three novel hardware architectures for microwave passive indoor applications. Experiments on vital sign monitoring and hand gesture detection demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed hardware topologies. These sensors might become reliable and affordable solutions for e-healthcare and ambient-assisted living for future indoor wireless applications, including passive vital sign tracking, passive presence detection, and passive gesture recognition.
The use of opportunistic RF sensors has a long history in military applications, airspace surveillance, and air traffic management. Passive or opportunistic microwave sensing devices detect and track targets by simultaneously analyzing the direct-path signals emitted from RF sources and the signals scattered from targets of interest. Because of the popularization of indoor communication networks, it is advantageous to design sensing systems that leverage ubiquitous signals transmitted by third-party transmitters. Furthermore, passive sensing technologies are a great alternative to avoid interference among different transceivers and to contribute to efficient spectrum usage. In contrast to most of the current results on indoor passive sensing that rely on existing hardware architectures exclusively designed for wireless communication purposes, I proposed three novel hardware architectures for microwave passive indoor applications. Experiments on vital sign monitoring and hand gesture detection demonstrated the effectiveness of the proposed hardware topologies. These sensors might become reliable and affordable solutions for e-healthcare and ambient-assisted living for future indoor wireless applications, including passive vital sign tracking, passive presence detection, and passive gesture recognition.
Structural Health Monitoring
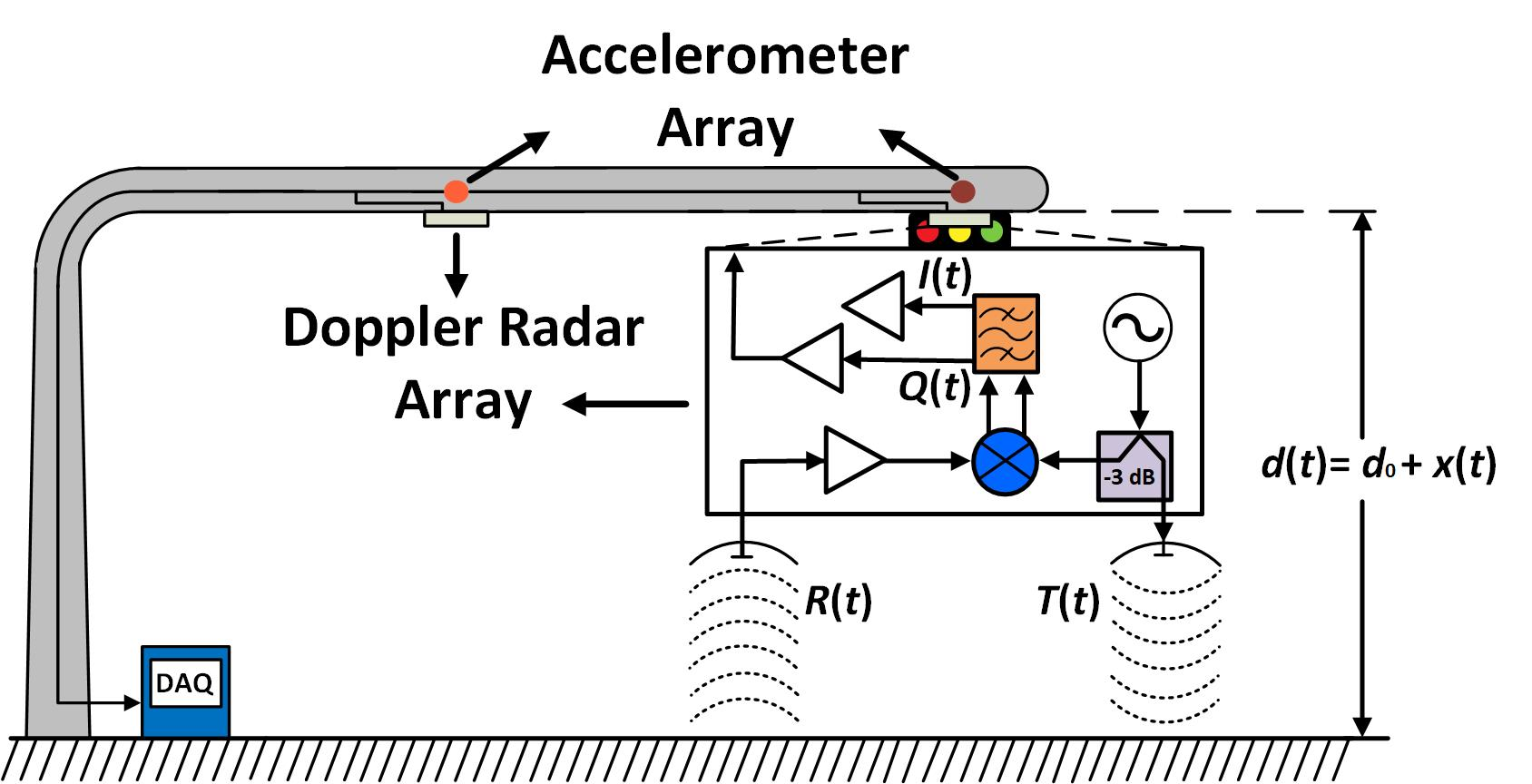 Structural health monitoring (SHM) is the implementation of measures for the condition assessment of structures such as bridges, wind turbines, and traffic lights. The deterioration of these structures is usually caused by aging, corrosion, or excessive loads. One of the main limitations of SHM based on radars is that the instantaneous magnitude of the noise levels might be large at times, which results in incorrect estimation of the displacement measurements. To overcome this challenge, I proposed signal processing algorithms for noise removal and displacement correction. After solving the fundamental noise coupling problem, a radar array was deployed to capture the deflections at several different locations of a traffic light. By doing so, other measurements such as operational modal analysis were obtained. Shifts on the structural natural frequency were also analyzed. Early warning on potential structural deterioration could be triggered if changes on the structural natural frequency or changes in the mode shapes are recognized.
Structural health monitoring (SHM) is the implementation of measures for the condition assessment of structures such as bridges, wind turbines, and traffic lights. The deterioration of these structures is usually caused by aging, corrosion, or excessive loads. One of the main limitations of SHM based on radars is that the instantaneous magnitude of the noise levels might be large at times, which results in incorrect estimation of the displacement measurements. To overcome this challenge, I proposed signal processing algorithms for noise removal and displacement correction. After solving the fundamental noise coupling problem, a radar array was deployed to capture the deflections at several different locations of a traffic light. By doing so, other measurements such as operational modal analysis were obtained. Shifts on the structural natural frequency were also analyzed. Early warning on potential structural deterioration could be triggered if changes on the structural natural frequency or changes in the mode shapes are recognized.
